How to Register a Business in Nigeria: A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Register a Business in Nigeria: A Step-by-Step Guide

Registering a business in Nigeria is critical for entrepreneurs, small business owners, and startups aiming to operate legally and sustainably. A registered business enjoys numerous benefits, including access to loans, enhanced customer credibility, and compliance with Nigerian laws. The Corporate Affairs Commission (CAC) is the official body responsible for business registration in Nigeria, ensuring that businesses are formally recognized and regulated.
Before you dive into the registration process, it’s crucial to understand the business structures recognized by the CAC. Choosing the proper structure can have long-term implications for your finances, liability, and operational flexibility.
This guide provides a comprehensive, step-by-step process to help you navigate the business registration process seamlessly.
Step 1: Understand the Types of Business Structures in Nigeria
Before registering your business, it’s essential to understand the different business structures recognized by the CAC. Each structure has unique features, advantages, and disadvantages:
I. Business Name (Sole Proprietorship or Partnership)
A business name registration is the most straightforward and affordable option for small business owners. It is ideal for those who want to operate under a unique business name without creating a separate legal entity.
• Sole Proprietorship: Owned and managed by one individual.
• Partnership: Owned by two or more individuals who share profits and liabilities.
a. Pros:
• Affordable registration process.
• Easy to set up
• Minimal regulatory requirements.
b. Cons:
• Unlimited liability (personal assets are at risk)
• Limited access to funding
• Less credibility with large clients
II. Limited Liability Company (LLC)
An LLC is the most common structure for medium to large businesses. It creates a separate legal entity, protecting owners or directors from personal liability.
a. Pros:
• Personal assets are protected from business liabilities.
• Attractive to investors and partners.
• Easier access to loans
• Suitable for scaling operations
• Greater credibility
b. Cons:
• Higher registration costs
• More regulatory requirements
• Complex setup process
• Requires compliance with annual filings and tax obligations.
III. Incorporated Trustees (for NGOs, Religious Organizations, etc.)
This structure is reserved for non-profits, religious organizations, and charities. It ensures that the organization operates with a clear legal framework.
a. Pros:
• Exemptions from certain taxes (in some cases).
• Offers transparency and credibility
• Legal recognition
• Eligibility for grants.
b. Cons:
• Longer registration process
• Requires detailed documentation of objectives and activities
• Strict regulatory oversight
• Limited to non-profit activities.
Choose the structure that aligns with your business goals, vision, and size, considering liability, scalability, and operational complexity factors.
Step 2: Prepare the Necessary Documents

To register your business, you’ll need the following documents:
1. Proposed Business Name(s): Provide at least two alternatives in case your first choice is unavailable.
a. Brainstorm Creative Names: Think of names that reflect your business’s identity, values, and services.
b. Use Online Tools: Utilize business name generators like Namecheap, Shopify, Namelix, Looka, or Canva for inspiration.
c. Engage Branding Professionals: Consult branding experts or agencies to help craft memorable, marketable, and legally compliant names tailored to your business vision.
2. Identification Documents: Valid ID (National ID, passport, or driver’s license) for all owners, partners, or directors.
3. Business Address: Proof of address for the business or registered office.
4. Memorandum and Articles of Association (for LLCs): These documents outline the company’s objectives, share structure, and internal regulations.
5. Passport Photographs: Recent passport-sized photos of the owners, partners, or directors.
Ensure all documents are accurate, up-to-date, and comply with CAC requirements to avoid delays.
Step 3: Conduct a Name Availability Search

Before proceeding with registration, verifying that your desired business name is available is important. The CAC’s online portal makes this process straightforward:
1. Visit the CAC website (https://www.cac.gov.ng).
2. Use the “Public Search” tool to check for existing businesses with similar names.
3. Ensure your chosen name adheres to CAC guidelines (avoid offensive words, government-related terms, or names already in use).
The name must be unique, not infringe on existing trademarks, and comply with CAC naming guidelines. Avoid names that are offensive, misleading, or similar to existing businesses. It’s also wise to pick a name that reflects your brand’s identity.
Step 4: Create an Account on the CAC Portal
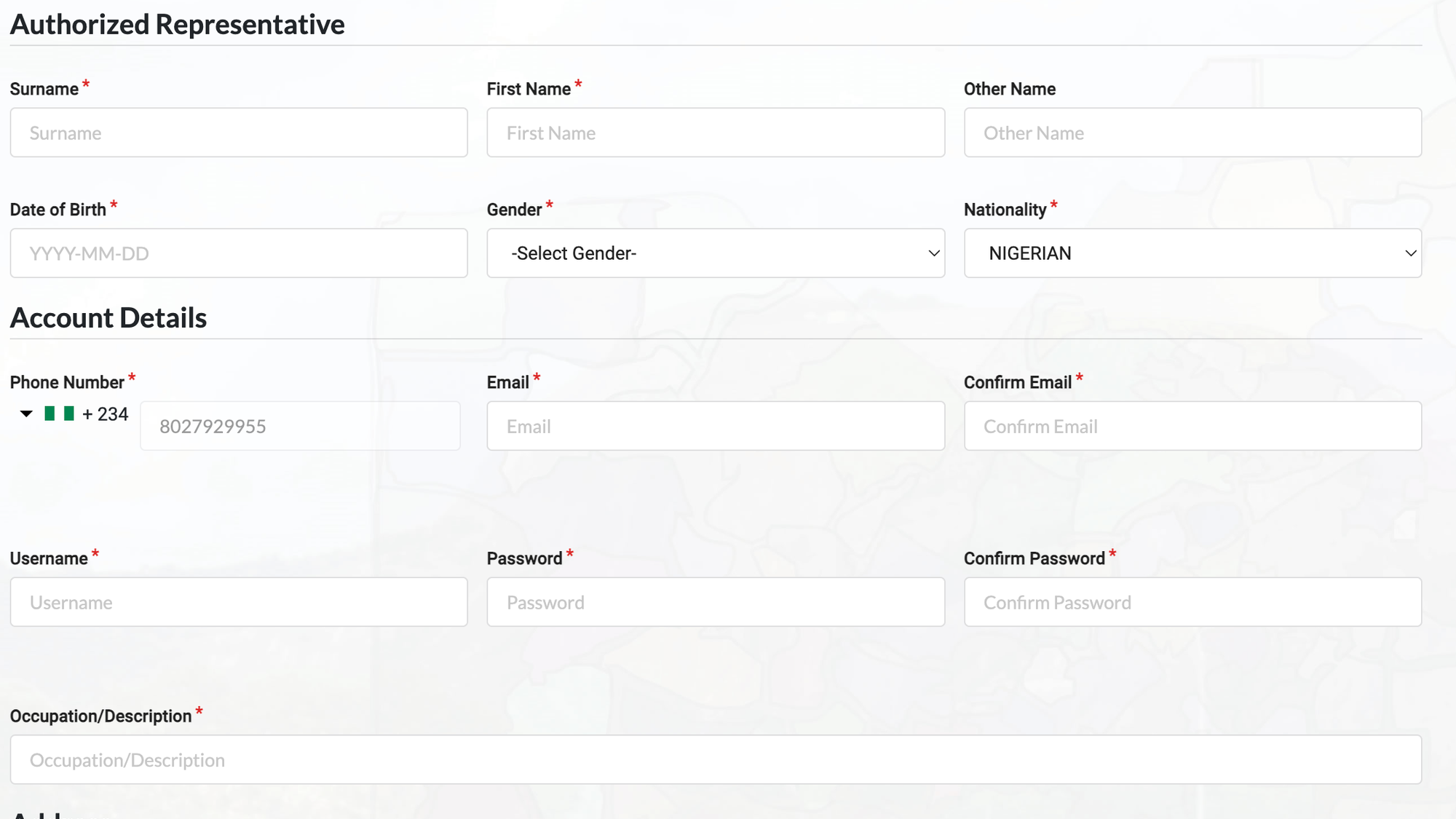
To begin the registration process, create an account on the CAC online platform:
1. Visit the CAC website (https://www.cac.gov.ng).
2. Click on “Register,” input your phone number or NIN, and fill in other required details (name, email, etc.).
3. For Non-Nigerians, toggle on the create account as a Non-Nigerian, and fill in other required details (name, email, etc.).
4. Verify your email address to activate your account.
5. Log in to your account to access the registration dashboard.
The portal is user-friendly, but ensure you have a stable internet connection and all necessary documents ready.
Step 5: Fill Out the Business Registration Form

The business registration form is the cornerstone of the entire process. Here’s how to complete it:
1. Business Details: Enter the business name, nature of business, and address.
2. Owner/Partner/Director Information: Provide details of all proprietors, partners, or directors, including their names, addresses, and identification numbers.
3. Upload Documents: Attach scanned copies of the required documents.
Accuracy is key. Double-check every field before submission to avoid processing delays or rejection.
Step 6: Pay the Required Fees

Business registration fees vary depending on the structure you’ve chosen. The CAC portal offers convenient payment options, including online payment via debit cards or bank transfers.
Payment can be made online via the CAC portal or offline at designated banks. Keep your payment receipt for reference, as it will be required for the next step.
Step 7: Submit the Application and Await Approval

After completing the form and paying the fees, submit your application. The CAC typically processes applications within 1–2 weeks, but delays may occur due to high volumes or incomplete submissions. Monitor your application status via the CAC portal. If corrections are required, the CAC will notify you.
Step 8: Obtain Your Certificate of Registration

Once approved, you’ll receive a notification to download or collect your Certificate of Registration. This document is proof of your business’s legal existence and should be kept safe. For LLCs, you’ll also receive the Memorandum and Articles of Association.
Step 9: Next Steps After Registration

After registering your business, take the following steps to operationalize and grow your venture fully:
1. Open a Corporate Bank Account: Use your Certificate of Registration to open a business bank account. This separates your personal and business finances, ensuring better financial management.
2. Register for Tax Identification Number (TIN): Visit the Federal Inland Revenue Service (FIRS) to obtain your TIN, which is essential for tax compliance and filing.
3. Set Up a Payment Gateway: Integrate a reliable payment gateway like Payaza (payaza.africa) to streamline transactions. Payaza enables seamless payments, helping you accept customer payments via cards, bank transfers, and POS.
4. Obtain Industry-Specific Permits: Depending on your business type, you may need to secure additional licenses or permits (e.g., health, safety, or environmental certifications) to operate legally.
5. File Annual Returns: Stay compliant by filing annual returns with the CAC and paying necessary taxes to avoid penalties.
By taking these steps, you’ll ensure your business is fully operational, compliant, and ready to scale. Leveraging tools like Payaza can also enhance your payment processes, improving customer experience and boosting revenue.
Registering a business in Nigeria is straightforward when you follow the right steps. By formalizing your business, you gain legal protection, access to funding, and credibility in the marketplace. Take the first step today and contribute to Nigeria’s growing economy. For further assistance, visit the CAC website (https://www.cac.gov.ng) or consult a legal professional.